Unix Interview Q&A -Part 1
Basic Unix Commands
cp , mv , cat , more , less , ls , wc , cut , sed , grep , find , awk
1.Describe the usage and functionality of the command “rm –r *” in UNIX?
Answer: The command “rm –r *” is a single line command to erase all files in a directory with its subdirectories.
- “rm” — command for deleting files.
- “-r” — command to delete directories and subdirectories with files within.
- “*” — indicates all entries.
2. What is the behavioral difference between “cmp” and “diff” commands?
Answer: Both commands are used for file comparison.
- Cmp — Compare given two files with byte by byte and display the first mismatch.
- Diff — Display changes that need to do to make both files identical.
3. What are the duties of the following commands: chmod, chown, chgrp?
Answer:
- chmod — Change the permission set of the file.
- chown — Change ownership of the file.
- chgrp — Change group of the file.
4. What is the purpose of the following command?
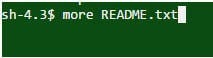
Answer: This command is used to display the first part of the file README.txt which just fits on one screen.
5. Describe the zip/unzip command using gzip?
Answer: gzip command creates a zip file using the given filename in the same directory.

gunzip command is used to unzip the file.

6. How to display the last line of a file?
Answer: This can be performed using either “tail” or “sed” commands. The easiest way is to use the “tail” command.

In the above example code, the last line of the README.txt is displayed.
7. What are the various IDs in UNIX processes?
Answer: Process ID is a unique integer that UNIX uses to identify each process. The process executes to initiate other processes is called parent process and its ID is defined as PPID (Parent Process ID).
getppid() — Is a command to retrieve PPID
Every process is associated with a specific user and is called the owner of the process. The owner has all the privileges over the process. The owner is also the user who executes the process.
Identification for a user is the User ID. The process is also associated with Effective User ID which determines the access privileges for accessing resources like files.
- getpid() — Retrieve process id
- getuid() — Retrieve user-id
- geteuid() — Retrieve effective user-id
8. How to Kill a process in UNIX?
Answer: The kill command accepts process ID (PID) as a parameter. This is applicable only for the processes owned by the command executor.
Syntax — kill PID
9. What is the command to find maximum memory taking process on the server?
Answer: Top command displays the CPU usage, process id, and other details.
10.What is the command to find hidden files in the current directory?
Answer: ‘ls –lrta’ command is used to display hidden files in the current directory.
11.Explain ‘nohup’ in UNIX?
Answer: “nohup” is a special command that is available to run a process in the background. The process starts with ‘nohup’ command and does not terminate even the user started to log off from the system.
12.What is the method to edit a large file without opening it in UNIX?
Answer: The “sed” command is available for this process ‘.sed’ stands for a team editor.
Example,

grep command: searches files for certain matching patterns.
Syntax: $grep pattern file(s)
Some of the options that are used along with grep command are enlisted below:
- -v: prints line that does not match the pattern.
- -n: print matched line and line number.
- -l: print file names with matching lines.
- -c: prints only count the matching lines.
- -i: matches either uppercase or lowercase.
13.How to remove the duplicate from file in unix
sort command: arranges lines of text alphabetically or numerically.
Passing this file to uniq will simply return the contents of the file. Where files are not already sorted the sort command can be used to sort the file first before piping to uniq. An article outlining the usage of sort is available here.
sort authors.txt | uniq
Chaucer
Orwell
Larkin14.How to show a count of the number of times a line occurred
To output the number of occurrences of a line use the -c option in conjunction with uniq. This prepends a number value to the output of each line.
uniq -c authors.txt
2 Chaucer
2 Larkin
1 Orwell15.How to only show repeated lines
To only show repeated lines pass the -d option to uniq. This will output only lines that occur more than once and write the result to standard output.
uniq -d authors.txt
Chaucer
Larkin16.How to only show lines that are not repeated
To only show lines that are not repeated pass the -u option to uniq. This will output only lines that are not repeated and write the result to standard output.
uniq -u authors.txt
Orwell17. Delete Files older Than 30 Days
find /opt/backup -type f -mtime +30find /opt/backup -type f -mtime +30 -delete
18. Delete Old Directory Recursively
find /var/log -type d -mtime +30 -exec rm -rf {} \;

.jpg)
No comments:
Post a Comment